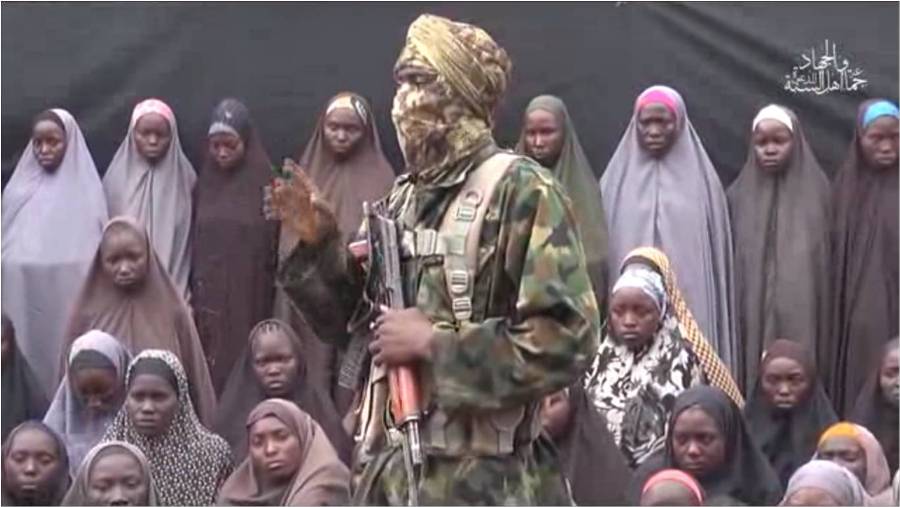
BuzzNigeria.com A video was released in August with new Boko Haram demands but YouTube removed it.

McClatchy: HOUSTON — A Texas oilman who’s accused of defrauding the Nigerian government by illegally pumping and exporting 10 million barrels of oil is a major fundraiser for Hillary Clinton’s presidential campaign.
Kase Lawal of Houston is at least the fourth person accused or convicted of criminal wrongdoing to help finance Clinton’s political ambitions since 2000 and the second in her quest for the White House. The list also includes Chinese and Pakistani fugitives and a former Miami lawyer who was convicted of defrauding Cuba.
There’s no indication that Clinton’s campaign was aware of Lawal’s legal problems when it accepted his help in raising more than $100,000, but a McClatchy investigation in the U.S. and Nigeria suggests that her campaign did little to scrutinize the background of one of its top fundraisers.
****
In 2010, Kase Lawal, Member, Advisory Committee for Trade Policy and Negotiations for the White House. CAMAC Energy, NYSE (CAK) was founded in 2005. CAMAC Energy Inc. has offices in Hartsdale, New York; Houston, Texas; Beijing, China and Lagos, Nigeria.
Lawal maxed out donations to Hillary’s 2016 primary campaign, and his wife Eileen donated $50,000—the most allowed—to President Obama’s 2009 inaugural committee.
Lawal describes himself as a devout Muslim who began memorizing the Quran at age 3 while attending an Islamic school. “Religion played a very important role in our lives,” he told a reporter in 2006. “Every time you finish a chapter they kill a chicken, and if you finish the whole thing, a goat.” In Africa, Lawal has been at the center of multiple criminal proceedings, even operating as a fugitive. Over the last decade, he faced charges in South Africa over an illegal oil scheme along with charges in Nigeria of illegally pumping and exporting 10 million barrels of oil.
Hillary Clinton Obstructed Boko Haram Terror Designation as Her Donors Cashed In
Source: Hillary Obstructed Boko Haram’s Terror Designation as Her Donors Cashed In | PJ Media
…as Boko Haram began to ramp up its terror campaign in 2011 and 2012, Hillary Clinton obstructed the official terror designation of the group over the objections of Congress, the FBI, the CIA and the Justice Department.
Why did Hillary Clinton’s State Department drag its feet on the terror designation in the face of near unanimous opposition from the rest of the U.S. government?
A recent series of reports exposes that a close Clinton family confidante — and Hillary campaign bundler — profited from Nigeria’s lucrative oil fields. He engaged in multiple illegal deals throughout Africa. …
Why is no one in the media talking about Hillary and Boko Haram?
It is worth nothing that Congress had to drag a reluctant State Department kicking and screaming to get Boko Haram designated in November 2013, after Hillary Clinton had left office.
Hillary Clinton’s willful obstruction in the matter is easy to document:
- Members of Congress discovered in 2014 that the Clinton State Department intentionally lied and downplayed the threat from Boko Haram, and worked to kill bills in both the House and the Senate calling for their designation in 2012.
- As Reuters reported, the Justice Department’s National Security Division strongly urged the State Department to designate Boko Haram, but then a group of 21 American academics rallied to the State Department’s aid by sending a letter to Hillary Clinton strongly arguing against Boko Haram’s designation.
- We also now know that the Obama administration was sitting on intelligence— obtained as a result of the Bin Laden raid— that revealed Boko Haram’s direct connection to al-Qaeda and the international terror network in 2011 and 2012. In other words, Hillary’s State Department was arguing that Boko Haram had no such connections, that it wasn’t a transnational terror threat, even though the Obama administration — and likely Clinton herself — knew that was false.
An important two-part investigative series by WORLD magazine reporters Mindy Belz and J.C. Derrick provides some insight:
Part 1 of our series on Clinton State Dept & Boko Haram @WORLD_maghttps://t.co/Vf1AezkhSF and Part 2 https://t.co/gUTv3yrruF#Nigeria
— Mindy Belz (@mcbelz) June 30, 2016
Belz and Derrick discovered that Hillary Clinton’s obstruction of the Boko Haram designation, and the continuing chaos in northern Nigeria — Africa’s largest economy and the 10th largest oil producer in the world — directly benefited Clinton Global Initiative donors and a close Clinton confidante who bundled campaign cash for Hillary.
From the second article from Belz and Derrick:
Perhaps the most prominent Nigerian with ties to the Clintons is Houston-based Kase Lawal. The founder of CAMAC Energy, an oil exploration and energy consortium, Lawal had a long history with Bill Clinton before becoming a “bundler” for Hillary’s 2008 presidential bid, amassing $100,000 in contributions and hosting a fundraiser in his Houston home — a 14-room, 15,264-square-foot mansion. Lawal maxed out donations to Hillary’s 2016 primary campaign, and his wife Eileen donated $50,000 — the most allowed — to President Obama’s 2009 inaugural committee.Lawal describes himself as a devout Muslim who began memorizing the Quran at age 3 while attending an Islamic school. “Religion played a very important role in our lives,” he told a reporter in 2006. “Every time you finish a chapter they kill a chicken, and if you finish the whole thing, a goat.”
Today the Houston oil exec — who retired in May as CEO but continues as chairman of the board of CAMAC, now called Erin Energy — tops the list of wealthiest Nigerians living in North America. His firm reports about $2.5 billion in annual revenue, making it one of the top private companies in the United States.
In Africa, Lawal has been at the center of multiple criminal proceedings, even operating as a fugitive. Over the last decade, he faced charges in South Africa over an illegal oil scheme along with charges in Nigeria of illegally pumping and exporting 10 million barrels of oil.
In the Democratic Republic of Congo, Lawal arranged a 2011 plot to purchase 4 tons of gold from a rebel warlord, Bosco Ntaganda, linked to massacres and mass rapes.Ntaganda was on a U.S. sanctions list, meaning anyone doing business with him could face up to 20 years in prison. Lawal contacted Clinton’s State Department, and authorities in Congo released his plane and associates in the plot.
He never faced charges in the United States, and he remains a commissioner for the Port Authority of Houston.
Lawal’s energy firm holds lucrative offshore oil licenses in Nigeria, as well as exploration and production licenses in Gambia, Ghana, and Kenya, where he operates in a conflict-ridden area largely controlled by Somalia’s al-Shabaab militants.
The firm also has held contracts in Nigeria for crude oil lifting, or transferring oil from its collection point to refineries. Until last year, when newly elected President Muhammadu Buhari began an effort to reform the process, contracting for lifting has been awash in kickbacks, bribes, and illegal activity.
Overland lifting contracts often involve partnership with the North’s past and present governors, including those who serve as quasi-warlords with ties to Boko Haram and other militants.
Lawal’s enterprises have long been rumored to be involved in such deals, as have indigenous oil concerns like Petro Energy and Oando, Nigeria’s largest private oil and gas company, based in Lagos and headed by Adewale Tinubu, another controversial Clinton donor.
In 2014, Oando pledged 1.5 percent of that year’s pre-tax profits and 1 percent of future profits to a Clinton Global Initiative education program. This year, Adewale gained notoriety when the Panama Papers revealed he holds at least 12 shell companies, leading to suspicion of money laundering, tax evasion, and other corruption.
In 2013 Bill Clinton stood alongside Adewale’s uncle, Bola Tinubu, while attending the dedication of a massive, controversial reclamation project called Eko Atlantic. Critics call Bola Tinubu, leader of the ruling All Progressives Congress party, Nigeria’s “looter in chief.” A Nigerian documentary says that when the billionaire landowner was governor of Lagos State (1999-2007), he funneled huge amounts of state funds — up to 15 percent of annual tax revenues — to a private consulting firm in which he had controlling interest.
In the United States, where he studied and worked in the 1970s and ’80s, Tinubu is still a suspect in connection with a Chicago heroin ring he allegedly operated with his wife and three other family members. In 1993 Tinubu forfeited $460,000 to American authorities, who believe he trafficked drugs and laundered the proceeds.
But wait, there’s more:
Beneath the surface, literally, Boko Haram was making it possible for illicit operators to lay claim to the area for their own purposes, and to pump oil from Nigeria’s underground reserves to Chad. Using 3-D drilling, Chad operators can extract Nigerian oil — without violating Nigerian property rights — to sell on open markets. One benefactor of the arrangement is Ali Modu Sheriff, a leading politician in the North, Borno State governor until 2011, and an alleged sponsor of Boko Haram, who is close friends with longtime Chad President Idriss Déby.The very terrorism that seems to be deterring oil exploration in reality can help illicit extraction, forcing residents to flee and giving cover to under-the-table oil traders. In 2015, a year when overall oil prices dipped 6 percent, Lawal’s Erin Energy stock value skyrocketed 295 percent—the best-performing oil and gas stock in the United States.
…
Hillary Clinton’s obstruction of the Boko Haram terror designation in the face of FBI, CIA, DOJ, and Congressional urging to do so is a documented fact. But the reason for Hillary’s obstruction, which the establishment media has never pressed Clinton for, remains unanswered.