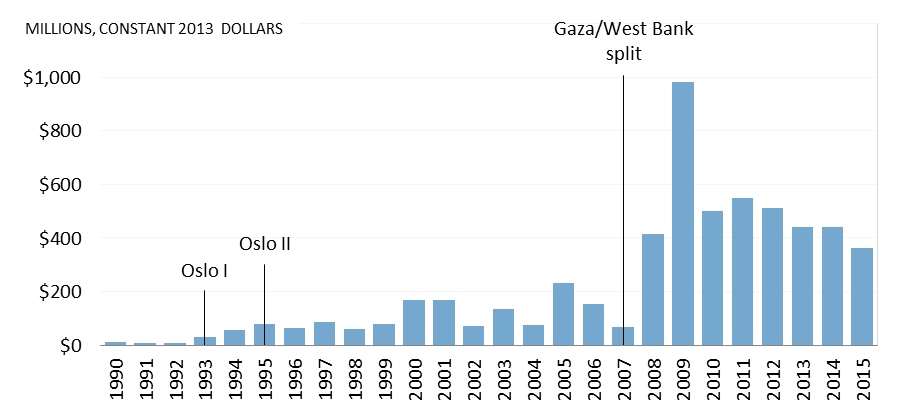
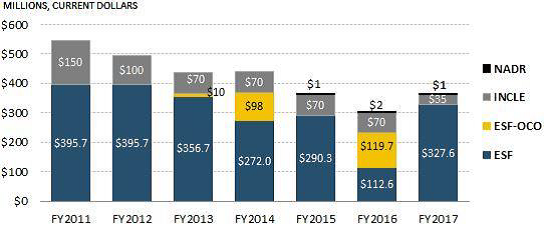
Note, that no NATO country was in attendance, note any American representation was not even consulted. This continues Russia’s hybrid-warfare tactics. Obama in mid-2015 announced a drawdown of troops in Afghanistan to an estimated 5500. That objective was delayed permanently. An investigation is underway that includes Tajikistan as being the weapons route for the Taliban from Russia.
***
AFP: Allegations over Russia and Iran’s deepening ties with the Taliban have ignited concerns of a renewed “Great Game” of proxy warfare in Afghanistan that could undermine US-backed troops and push the country deeper into turmoil.
Moscow and Tehran insist their contact with insurgents is aimed at promoting regional security, but local and US officials who are already frustrated with Pakistan’s perceived double-dealing in Afghanistan have expressed bitter scepticism.
Washington’s long-time nemesis Iran is accused of covertly aiding the Taliban, and Russia is back to what observers call Cold War shenanigans to derail US gains at a time when uncertainty reigns over President-elect Donald Trump’s Afghanistan policy.
***
The US will slow its troop drawdown in Afghanistan, leaving a force of 8,400 when President Barack Obama completes his term, the president announced on Wednesday in a blunt acknowledgment that America will remain entangled there despite his aspirations to end the war.
In a statement at the White House, Mr Obama said the security situation in Afghanistan is “precarious” and the Taliban remain a threat roughly 15 years after the US invaded in the aftermath of 9/11. He said he was committed not to allow any group to use Afghanistan “as a safe haven for terrorists to attack our nation again.”
“It is in our national security interest – especially after all the blood and treasure we’ve invested in Afghanistan over the years – that we give our Afghan partners the very best opportunity to succeed,” Mr Obama said, flanked by top military leaders.
Mr Obama has been under pressure from US allies to make a decision following a NATO announcement last month that the alliance would maintain troops in regional locations around Afghanistan. NATO’s future involvement in the fight is to be a major topic when Mr Obama attends a NATO summit later this week in Warsaw, Poland.
Mr Obama said boosting the planned troop levels would help other countries prepare their own contribution to the fight. He said his decision should help the next president make good decisions about the future of US involvement.
“l firmly believe the decision I’m announcing is the right thing to do,” Mr Obama said. More here.
Russia’s New Favorite Jihadis: The Taliban
More than 15 years into America’s war in Afghanistan, the Russian government is openly advocating on behalf of the Taliban.
Last week, Moscow hosted Chinese and Pakistani emissaries to discuss the war. Tellingly, no Afghan officials were invited. However, the trio of nations urged the world to be “flexible” in dealing with the Taliban, which remains the Afghan government’s most dangerous foe. Russia even argued that the Taliban is a necessary bulwark in the war against the so-called Islamic State.
For its part, the American military sees Moscow’s embrace of the Taliban as yet another move intended to undermine NATO, which fights the Taliban, al Qaeda, and the Islamic State every day.
After Moscow’s conference, Russian Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova spoke with reporters and noted that “the three countries expressed particular concern about the rising activity in the country of extremist groups, including the Afghan branch of IS [the Islamic State, or ISIS].”
According to Reuters, Zakharova added that China, Pakistan, and Russia agreed upon a “flexible approach to remove certain [Taliban] figures from [United Nations] sanctions lists as part of efforts to foster a peaceful dialogue between Kabul and the Taliban movement.”
The Taliban, which refers to itself as the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, quickly praised the “Moscow tripartite” in a statement posted online on Dec. 29.
“It is joyous to see that the regional countries have also understood that the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan is a political and military force,” Muhammad Sohail Shaheen, a spokesman for the group’s political office, said in the statement. “The proposal forwarded in the Moscow tripartite of delisting members of the Islamic Emirate is a positive step forward in bringing peace and security to Afghanistan.”
Of course, the Taliban isn’t interested in “peace and security.” The jihadist group wants to win the Afghan war and it is using negotiations with regional and international powers to improve its standing. The Taliban has long manipulated “peace” negotiations with the U.S. and Western powers as a pretext for undoing international sanctions that limit the ability of its senior figures to travel abroad for lucrative fundraising and other purposes, even while offering no serious gestures toward peace.
The Obama administration has repeatedly tried, and failed, to open the door to peace. In May 2014, the U.S. transferred five senior Taliban figures from Guantanamo to Qatar. Ostensibly, the “Taliban Five” were traded for Sgt. Bowe Bergdahl, an American who reportedly deserted his fellow soldiers and was then held by the Taliban and its jihadist allies. But the Obama administration also hoped that the exchange would be a so-called confidence-building measure and lead to more substantive negotiations. The Taliban’s leaders never agreed to any such discussions. They simply wanted their comrades, at least two of whom are suspected of committing war crimes, freed from Guantanamo.
Regardless, Russia is now enabling the Taliban’s disingenuous diplomacy by pretending that ISIS is the more worrisome threat. It’s a game the Russians have been playing for more than a year.
In December 2015, Zamir Kabulov, who serves as Vladimir Putin’s special representative for Afghanistan, went so far as to claim that “the Taliban interest objectively coincides with ours” when it comes to fighting ISIS head Abu Bakr al Baghdadi’s loyalists. Kabulov even conceded that Russia and the Taliban have “channels for exchanging information,” according to The Washington Post.
The American commanders leading the fight in Afghanistan don’t buy Russia’s argument—at all.
During a press briefing on Dec. 2, General John W. Nicholson Jr., the commander of NATO’s Resolute Support and U.S. Forces in Afghanistan, discussed “the malign influence of external actors and particularly Pakistan, Russia, and Iran.” Gen. Nicholson said the U.S. and its allies are “concerned about the external enablement of the insurgent or terrorist groups inside Afghanistan, in particular where they enjoy sanctuary or support from outside governments.” Russia, in particular, “has overtly lent legitimacy to the Taliban.”
According to Nicholson, the Russian “narrative” is “that the Taliban are the ones fighting the Islamic State, not the Afghan government.” While the Taliban does fight its jihadist rivals in the Islamic State, this is plainly false.
The “Afghan government and the U.S. counterterrorism effort are the ones achieving the greatest effect against Islamic State,” Nicholson said. He went on to list the U.S.-led coalition’s accomplishments over the past year: 500 ISIS fighters (comprising an estimated 25 to 30 percent of the group’s overall force structure) were killed or wounded, the organization’s “top 12 leaders” (including its emir, Hafiz Saeed Khan) were killed, and the group’s “sanctuary” has been reduced from nine Afghan districts to just three.
“So, this public legitimacy that Russia lends to the Taliban is not based on fact, but it is used as a way to essentially undermine the Afghan government and the NATO effort and bolster the belligerents,” Nicholson concluded. While Nicholson was careful not read too much into Russia’s motivation for backing the Taliban, he noted “certainly there’s a competition with NATO.”
There’s no doubt that ISIS’s operations in Afghanistan grew significantly in the wake of Baghdadi’s caliphate declaration in 2014. However, as Nicholson correctly pointed out, Baghdadi’s men are not adding to the territory they control at the moment. Their turf is shrinking. The same cannot be said for the Taliban, which remains the most significant threat to Afghanistan’s future. At any given time, the Taliban threatens several provincial capitals. The Taliban also controls dozens of Afghan districts and contests many more. Simply put, the Taliban is a far greater menace inside Afghanistan than Baghdadi’s men.
Regardless, the Russians continue to press their case. Their argument hinges on the idea that ISIS is a “global” force to be reckoned with, while the Taliban is just a “local” nuisance.
Kabulov, Putin’s special envoy to Afghanistan, made this very same claim in a newly-published interview with Anadolu Agency. Kabulov contends that “the bulk, main leadership, current leadership, and the majority of Taliban” are now a “local force” as a “result of all these historical lessons they got in Afghanistan.”
“They gave up the global jihadism idea,” Kabulov adds. “They are upset and regret that they followed Osama bin Laden.”
Someone should tell the Taliban’s media department this.
Earlier this month, the Taliban released a major documentary video, “Bond of Nation with the Mujahideen.” The video included clips of the Taliban’s most senior leaders rejecting peace talks and vowing to wage jihad until the end. It also openly advertised the Taliban’s undying alliance with al Qaeda. At one point, an image of Osama bin Laden next to Taliban founder Mullah Omar is displayed on screen. Photos of other al Qaeda and Taliban figures are mixed together in the same shot.
An audio message from Sheikh Khalid Batarfi, an al Qaeda veteran stationed in Yemen, is also played during the video. Batarfi praised the Taliban for protecting bin Laden even after the Sept. 11, 2001 hijackings. “Groups of Afghan Mujahideen have emerged from the land of Afghans that will destroy the biggest idol and head of kufr of our time, America,” Batarfi threatened.
A narrator added that the mujahideen in Afghanistan “are the hope of Muslims for reviving back the honor of the Muslim Ummah [worldwide community of Muslims]!” The Afghan jihadists are a “hope for taking back the Islamic lands!” and a “hope for not repeating defeats and tragedies of the last century!”
The Taliban’s message is, therefore, unmistakable: The war in Afghanistan is part of the global jihadist conflict.
All of this, and more, is in one of the Taliban’s most important media productions of 2016. There is no hint that the Taliban “regrets” allying with al Qaeda, or has given “up the global jihadism idea,” as Kabulov claims. The exact opposite is true.
There is much more to the Taliban-al Qaeda nexus. In August 2015, al Qaeda honcho Ayman al Zawahiri swore allegiance to Mullah Mansour, who was named as Mullah Omar’s successor as the Taliban’s emir. Mansour publicly accepted Zawahiri’s fealty and Zawahiri’s oath was prominently featured on the Taliban’s website. After Mansour was killed earlier this year, Zawahiri pledged his allegiance to Mansour’s replacement, Mullah Haibatullah Akhundzada. Zawahiri and other al Qaeda leaders regularly call upon Muslims to support the Taliban and reject the Islamic State’s Afghan branch.
In his interview with Anadolu Agency, Kabulov concedes that not all of the Taliban has “given up” the global jihadist “ideas.” He admits that within the Taliban “you can find very influential groups like the Haqqani network whose ideology is more radical, closer to Daesh [or ISIS].”
Kabulov is right that the Haqqanis are committed jihadi ideologues, but he misses the obvious contradiction in his arguments. Siraj Haqqani, who leads the Haqqani network, is also one of the Taliban’s top two deputy leaders. He is the Taliban’s military warlord. Not only is Siraj Haqqani a “radical” ideologue, as Kabulov mentions in passing, he is also one of al Qaeda’s most committed allies. Documents recovered in Osama bin Laden’s compound show that al Qaeda’s men closely cooperate with Siraj Haqqani on the Afghan battlefields.
Kabulov claims that ISIS “operates much more smartly” than al Qaeda and has “learned from all the mistakes of al Qaeda.” He says Baghdadi’s enterprise has “brought more advanced and sophisticated people to design, plan, and [execute] policy.” Once again, the exact opposite is true.
Al Qaeda has long known the pitfalls of ISIS’s in-your-face strategy, and has smartly decided to hide the extent of its influence and operations. Zawahiri and his lieutenants have also used ISIS’s over-the-top brutality to market themselves as a more reasonable jihadi alternative. And both the Taliban and al Qaeda are attempting to build more popular support for their cause as much of the world remains focused on the so-called caliphate’s horror show.
Al Qaeda’s plan has worked so well that the Russians would have us believe that the Taliban, al Qaeda’s longtime ally, should be viewed as a prospective partner.
Kabulov says that Russia is waiting to see how the “new president, [Donald] Trump, describe[s] his Afghan policy” before determining what course should be pursued next.
Here’s one thing the Trump administration should do right away: Make it clear that the Taliban and al Qaeda remain our enemies in Afghanistan.