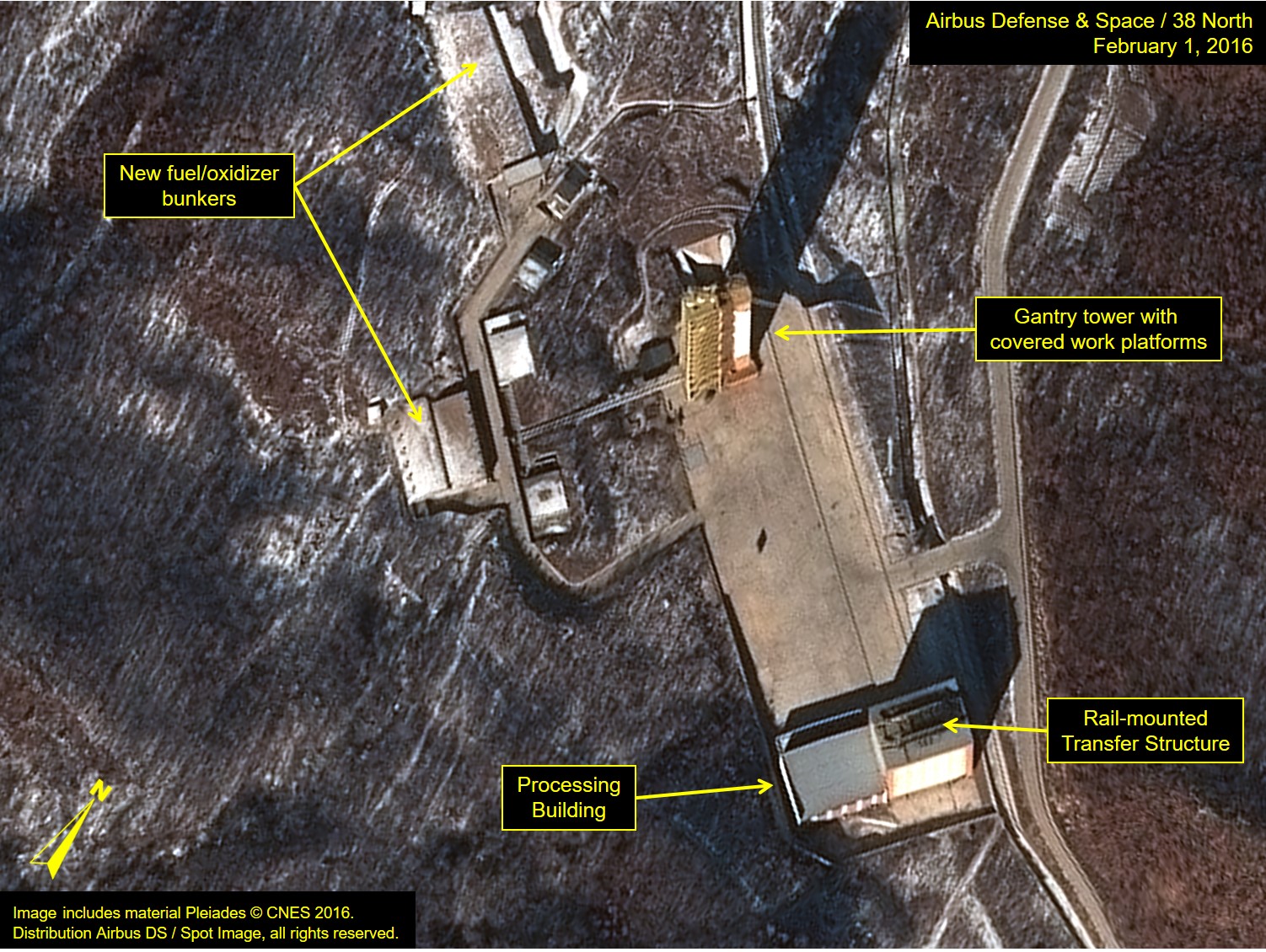
You have been profiled, but is it accurate? You have been sold and sold out.
Scary New Ways the Internet Profiles You
The success of the consumer Internet can be attributed to a simple grand bargain. We’ve been encouraged to search the web, share our lives with friends, and take advantage of all sorts of other free services. In exchange, the Internet titans that provide these services, as well as hundreds of other lesser-known firms, have meticulously tracked our every move in order to bombard us with targeted advertising. Now, this grand bargain is being tested by new attitudes and technologies.
Consumers who were not long ago blithely dismissive of privacy issues are increasingly feeling that they’ve lost control over their personal information. Meanwhile, Internet companies, adtech firms, and data brokers continue to roll out new technologies to build ever more granular profiles of hundreds of millions, if not billions, of consumers. And with next generation of artificial intelligence poised to exploit our data in ways we can’t even imagine, the simple terms of the old agreement seem woefully inadequate.
In the early days of the Internet, we were led to believe that all this data would deliver us to a state of information nirvana. We were going to get new tools and better communications, access to all the information we could possibly need, and ads we actually wanted to receive. Who could possibly argue with that?
For a while, the predictions seemed to be coming true. But then privacy goalposts were (repeatedly) moved, companies were caught (accidentally) snooping on us, and hackers showed us just how easy it is to steal our personal information. Advertisers weren’t thrilled either, particularly when we adopted mobile phones and tablets. That’s because the cookies that track us on our computers don’t work very well on mobile devices. And with our online activity split among our various devices, each of us suddenly appeared to be two or three different people.
This wasn’t a bad thing for consumers, because mobile phones emit data that enable companies to learn new things about us, such as where we go, who we meet, places we shop, and other habits that help them recognize and then predict our long-term patterns.
But now, new cross-device technologies are enabling the advertising industry to combine all our information streams into a single comprehensive profile by linking each of us to our desktop, mobile phone, and iPad. Throw in wearable devices like a Fitbit, connected TVs, and the Internet of Things, and the concept of cross-device tracking expands to potentially include anything that gives off a signal.
The ad industry is drooling over this technology because it can follow and target us as we move through our daily routines, whether we are searching on our desktop, surfing on our iPad, or out on the town with our phone in hand.
There are two methods to track people across devices. The more precise technique is deterministic tracking, which links devices to a single user when that person logs into the same site from a desktop computer, phone, and tablet. This is the approach used by Internet giants like Facebook, Twitter, Google, and Apple, all of which have enormous user bases that log into their mobile and desktop properties.
A quick glance at Facebook’s data privacy policy shows it records just about everything we do, including the content we provide, who we communicate with, what we look at on its pages, as well as information about us that our friends provide. Facebook saves payment information, details about the devices we use, location info, and connection details. The social network also knows when we visit third-party sites that use its services (such as the Like button, Facebook Log In, or the company’s measurement and advertising services). It also collects information about us from its partners.
Most of the tech giants have similar policies and they all emphasize that they do not share personally identifiable information with third parties. Facebook, for example, uses our data to deliver ads within its walled garden but says it does not let outsiders export our information. Google says it only shares aggregated sets of anonymized data.
Little-known companies—primarily advertising networks and adtech firms like Tapad and Drawbridge—are also watching us. We will never log into their websites, so they use probabilistic tracking techniques to link us to our devices. They start by embedding digital tags or pixels into the millions of websites we visit so they can identify our devices, monitor our browsing habits, look for time-based patterns, as well as other metrics. By churning massive amounts of this data through statistical models, tracking companies can discern patterns and make predictions about who is using which device. Proponents claim they are accurate more than 90 percent of the time, but none of this is visible to us and is thus very difficult to control.
In recent comments to the Federal Trade Commission, the Center for Democracy and Technology illustrated just how invasive cross-device tracking technology could be. Suppose a user searched for sexually transmitted disease (STD) symptoms on her personal computer, used a phone to look up directions to a Planned Parenthood clinic, visited a pharmacy, and then returned home. With this kind of cross-device tracking, it would be easy to infer that the user was treated for an STD.
That’s creepy enough, but consider this: by using the GPS or WiFi information generated by the patient’s mobile phone, it would not be difficult to discover her address. And by merging her online profile with offline information from a third-party data broker, it would be fairly simple to identify the patient.
So, should we be concerned that companies use cross-device tracking to compile more comprehensive profiles of us? Let us count the reasons:
Your data could be hacked: Privacy Rights Clearinghouse reports that in 2015 alone, hackers gained access to the records of 4.5 million patients at UCLA Health System, 37 million clients of online cheating website Ashley Madison, 15 million Experian accounts, 80 million Anthem customers, as well as more than 21 million individuals in the federal Office of Personnel Management’s security clearance database. And these were just the headliners that garnered media attention. No site or network is entirely safe and numerous researchers have already demonstrated how incredibly easy it is to “reidentify” or “deanonymize” individuals hidden in anonymized data.
Your profile could be sold: In fact, it typically is, in anonymized fashion. That’s the whole point. But in many cases, Internet companies’ privacy policies also make it clear our profiles are assets to be bought and sold should the company change ownership. This was the case when Verizon bought AOL and merged their advertising efforts, creating much more detailed profiles of their combined user base. Yahoo might be next should it decide to spin off its Internet properties.
Your data could be used in ways you did not anticipate: Google, Facebook, and other companies create customized web experiences based on our interests, behavior, and even our social circles. On one level, this makes perfect sense because none of us want to scroll through reams of irrelevant search results, news stories, or social media updates. But researchers have demonstrated that our online profiles also have real world consequences, including the prices we pay for products, the amount of credit extended to us, and even the job offers we may receive.
Our data is already used to build and test advanced analytics models for new services and features. There is much more to come. The Googles and the Facebooks of the Internet boast that newly emerging artificial intelligence will enable them to analyze greater amounts of our data to discern new behavioral patterns and to predict what we will think and want before we actually think and want it. These companies have only begun to scratch the surface of what is possible with our data.
We are being profiled in incredible and increasingly detailed ways, and our data may be exploited for purposes we cannot yet possibly understand. The old bargain—free Internet services in exchange for targeted advertising—is rapidly become a quaint relic of the past. And with no sense of how, when, or why our data might be used in the future, it is not clear what might take its place.