Notable projects in the U.S. include:
The first Brazilian company to complete a public project in the country, Odebrecht celebrates 20 years of operations in the United States in 2010. The construction company has completed 55 projects throughout its history and is currently present in Florida and Louisiana. In the country, Odebrecht has also been in California, North Carolina and South Carolina.
Odebrecht arrived to U.S. soil after it won the public bid to build a stretch of the Metromover, Miami’s above-ground subway. Soon after, in 1992, Odebrecht was responsible for building Route 56, a highway in the region of San Diego, California.
After these projects, the rhythm of the work continued to be intense. The following year, after winning the bid to work on the Santa Ana River chute, the company earned an important contract: The Seven Oaks Dam project in California, in the amount of US$ 168 million, with a construction period of 52 months. During this same year, 1993, the Company was responsible for the construction work on the Merrill Barber Bridge and the Golden Glades viaduct, which extends 2,464 meters to serve those who use the I-95 system, the federal highway that goes from Southern Florida to Canada. As a result of these experiences, Odebrecht was chosen to erect Garcon Point Bridge in Santa Rosa Bay, at the border between Florida and Alabama.
In the building construction area, Odebrecht was responsible for the American Airlines Arena, a sports and cultural complex in Miami, where it competed for the contract with major U.S. companies. It also built the Fortune House building, an apart hotel with 29 floors, the Ocean Steps building, with 15 residential floors, and the Ritz Carlton Key Biscayne Resort & Spa, a residential hotel project.
One of the company’s main clients is Miami-Dade County – with projects in the sector of aviation and mass transportation. The partnership has existed since 1993, when the construction company was responsible for building the American Airlines cargo building. Currently, Odebrecht is responsible for expanding the North Terminals of the Miami International Airport, building the lightweight vehicle that will run on the tracks (Mia Mover) and extending the subway (Airport Link).
The North Terminal Development Program, which involves investments of US$ 2.85 billion, is the center of a bigger venture, worth US$ 6.2 billion, called the “Capital Improvement Program.” Undertaken by Miami-Dade County, it was developed with aims of expanding and improving the aviation system. The complete project includes 52 new gates, four train stations, new installations for the United States Immigration and Citizenship Services, 123 counters, 119 self-service kiosks, 72 federal inspection service posts and a new luggage system. In September, the Sky Train operation began running, connecting the ends of the four main areas of the North Terminal in under five minutes. It is estimated that the program will be completed in 2011, while the construction work for the South Terminal began in 2001 and was completed in 2007. The project included Concourse J, a lobby with 15 departure gates for national and international flights, Concourse H, which already existed and was modernized, as well as a patio that surrounds the area of these buildings.
Also at the Miami International Airport, Odebrecht is heading the construction of the MIA Mover, an automatic vehicle that runs on tracks and will connect the Miami International Airport (MIA) to the Miami Intermodal Center (MIC), a terminal that connects different transportation services. The development, the result of a US$ 256 million investment, will be completed in September 2011.
Another project underway is the construction of the Airport Link, which will connect MIC at the airport to the Earlington Heights subway station. With an investment of US$ 360 million, the project extends nearly four kilometers, with the construction of three subway substations, a bus stop and highway access points.
Odebrecht was also at the Orlando Airport, working on the North Transversal taxi strip and South Terminal Complex. The project also involved the construction of access ramps and new viaducts.
In New Orleans since 2006, Odebrecht won two new contracts in 2010 in the city. In August, it signed a contract with the US Army Corps of Engineers to undertake preventive construction work for floods. In May, the company began constructing four water pumping stations, with aims of preventing floods caused by hurricanes. Recently, the company also delivered projects at Cataouatche Lake and in the region of Chalmette, work designed to reconstruct and fortify containment dikes. The construction works are part of the Hurricane Storm Damage Risk Reduction System (HSDRRS), which consists of 250 different projects and involves total investments of US$ 15 billion.
Main Completed Projects
South Terminal of the Miami International Airport – Miami, Florida
Containment Dike at Lake Cataouatche – New Orleans, Louisiana
Containment Dike at Chalmette Loop – New Orleans, Louisiana
American Airlines Arena – Miami, Florida
Expansion of the FIU Football Stadium
Expansion of the Northeast Terminal of the Orlando International Airport – Miami, Florida
Seven Oaks Dam – San Bernardino, California
Carnival Center for the Performing Arts – Miami, Florida
Miami International Airport Dolphin Garage Building – Miami, Florida
M-DWASD Head Office – Coral Gables, Florida
South Road System Extension – Miami International Airport – Miami, Florida
Miami International Airport North Terminal Extension – Miami, Florida
Fine Air Hangar at the Miami International Airport – Miami, Florida
Metromover – Miami, Florida
Western “U” Apron at the Miami International Airport – Miami, Florida
Fort Lauderdale International Airport Yard – Fort Lauderdale, Florida
Merrill Barber Bridge – Vero Beach, Florida
Santa Rosa Bridge – Santa Rosa County, Florida
Ritz-Carlton Key Biscayne Resort & Spa – Miami, Florida
Route 56 – San Diego, California
Miami International Airport Lobby “A” – Miami, Florida
American Airlines Terminal – Miami, Florida
Federal Express Terminal – Miami, Florida
Challenge Air Cargo Terminal – Miami, Florida
Miami International Airport Western “U” Cargo Terminal – Miami, Florida
Miami International Airport Control Tower – Miami, Florida
Golden Glades Viaduct – Miami, Florida
Odebrecht Organization
Founded in Bahia in 1944, Odebrecht Engenharia & Construção is currently the largest company in the sector in Latin America. With earnings of over R$ 18.7 billion in 2009, 70% of its revenues originate from projects abroad. It is present on the three Americas, Africa, Europe and the Middle East, and employs some 87,000 people.
The company, which has already completed nearly 2,000 projects in 35 different countries, provides integrated services in the areas of engineering, supply, construction, assembly and management of projects in the civil construction, industrial and special technology areas. Odebrecht Engineering & Construction includes six companies, consolidated in 2010, based on the business or geographic area of operations: Odebrecht Energia, Odebrecht Industrial, Odebrecht Infraestrutura, Odebrecht Latin America and Angola, Odebrecht Venezuela and Odebrecht International.
In 2009, Odebrecht finished building the Doraleh container terminal in Djibuti, and started the construction work to rebuild over 240 km of railroad for Arcelor Mittal in Liberia. Among its current projects, worthy of note are the Tripoli Airport (Libya) and the construction of an ethanol plant in Ghana.
The Bribery Schemes
According to its admissions, Odebrecht engaged in a massive and unparalleled bribery and bid-rigging scheme for more than a decade, beginning as early as 2001. During that time, Odebrecht paid approximately $788 million in bribes to government officials, their representatives and political parties in a number of countries in order to win business in those countries. The criminal conduct was directed by the highest levels of the company, with the bribes paid through a complex network of shell companies, off-book transactions and off-shore bank accounts.
As part of the scheme, Odebrecht and its co-conspirators created and funded an elaborate, secret financial structure within the company that operated to account for and disburse bribe payments to foreign government officials and political parties. By 2006, the development and operation of this secret financial structure had evolved such that Odebrecht established the “Division of Structured Operations,” which effectively functioned as a stand-alone bribe department within Odebrecht and its related entities. Until approximately 2009, the head of the Division of Structured Operations reported to the highest levels within Odebrecht, including to obtain authorization to approve bribe payments. After 2009, this responsibility was delegated to certain company business leaders in Brazil and the other jurisdictions. To conceal its activities, the Division of Structured Operations utilized an entirely separate and off-book communications system, which allowed members of the Division of Structured Operations to communicate with one another and with outside financial operators and other co-conspirators about the bribes via secure emails and instant messages, using codenames and passwords.
The Division of Structured Operations managed the “shadow” budget for the Odebrecht bribery operation via a separate computer system that was used to request and process bribe payments as well as to generate and populate spreadsheets that tracked and internally accounted for the shadow budget. These funds for the company’s sophisticated bribery operation were generated by the Odebrecht Finance Department through a variety of methods, as well as by certain Odebrecht subsidiaries, including Braskem. The funds were then funneled by the Division of Structured Operations to a series of off-shore entities that were not included on Odebrecht’s balance sheet as related entities. The Division of Structured Operations then directed the disbursement of the funds from the off-shore entities to the bribe recipient, through the use of wire transfers through one or more of the off-shore entities, as well as through cash payments both inside and outside Brazil, which were sometimes delivered using packages or suitcases left at predetermined locations.
Odebrecht, its employees and agents took a number of steps while in the United States to further the scheme. For instance, in 2014 and 2015, while located in Miami, two Odebrecht employees engaged in conduct related to certain projects in furtherance of the scheme, including meetings with other co-conspirators to plan actions to be taken in connection with the Division of Structured Operations, the movement of criminal proceeds and other criminal conduct. In addition, some of the off-shore entities used by the Division of Structured Operations to hold and disburse unrecorded funds were established, owned and/or operated by individuals located in the United States. In all, this conduct resulted in corrupt payments and/or profits totaling approximately $3.336 billion.
Braskem also admitted to engaging in a wide-ranging bribery scheme and acknowledged the pervasiveness of its conduct. Between 2006 and 2014, Braskem paid approximately $250 million into Odebrecht’s secret, off-book bribe payment system. Using the Odebrecht system, Braskem authorized the payment of bribes to politicians and political parties in Brazil, as well as to an official at Petróleo Brasileiro S.A. – Petrobras (Petrobras), the state-controlled oil company of Brazil. In exchange, Braskem received various benefits, including: preferential rates from Petrobras for the purchase of raw materials used by the company; contracts with Petrobras; and favorable legislation and government programs that reduced the company’s tax liabilities in Brazil. This conduct resulted in corrupt payments and/or profits totaling approximately $465 million.



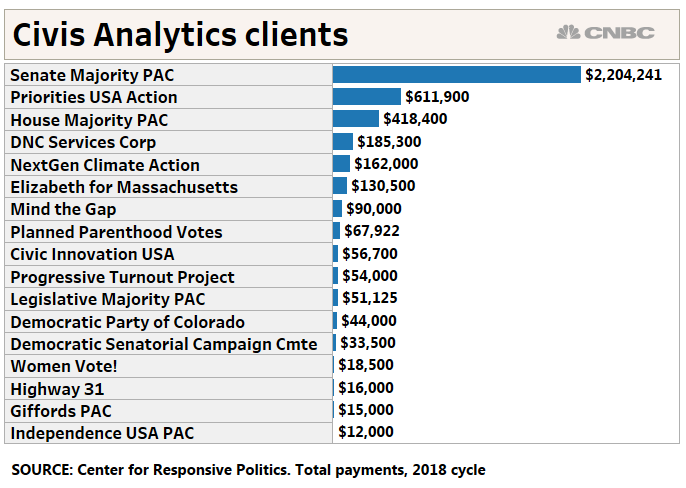 Where is some of these social justice policy concepts coming from that were introduced at both Democrat debates? Yet another project also tied to Civis Analytics call The New Progressive Agenda Project.
Where is some of these social justice policy concepts coming from that were introduced at both Democrat debates? Yet another project also tied to Civis Analytics call The New Progressive Agenda Project. Elias and Podesta
Elias and Podesta