 According to Wikipedia, Teneo is an US-based global advisory firm that partners exclusively with the Chief Executive Officers and senior leaders of many of the world’s largest and most complex companies and organizations.[3] The firm works with clients to address a wide range of financial, reputational and transformational challenges and has opportunities by combining the disciplines of strategic communications, investor relations, investment banking, financial analytics, executive recruiting, digital analytics, corporate governance, government affairs, business intelligence, management consulting and corporate restructuring on an integrated basis. Teneo’s clients include the CEOs of many Fortune 100 companies across a diverse range of industry sectors.
According to Wikipedia, Teneo is an US-based global advisory firm that partners exclusively with the Chief Executive Officers and senior leaders of many of the world’s largest and most complex companies and organizations.[3] The firm works with clients to address a wide range of financial, reputational and transformational challenges and has opportunities by combining the disciplines of strategic communications, investor relations, investment banking, financial analytics, executive recruiting, digital analytics, corporate governance, government affairs, business intelligence, management consulting and corporate restructuring on an integrated basis. Teneo’s clients include the CEOs of many Fortune 100 companies across a diverse range of industry sectors.
I N T E G R AT E D C O U N S E L F O R A B O R D E R L E S S WO R L D
From Politico, The four businesses of Teneo — which provides integrated counsel to a client list that includes FORTUNE 500 companies, philanthropies, governments and high net worth individuals – are Teneo Capital, Teneo Restructuring, Teneo Strategy and Teneo Intelligence. Ed Rollins recently joined as a public-affairs adviser.
From PRNewswire: New York City Police Commissioner Bill Bratton To Join Teneo
Teneo to launch new operating division advising major global companies and organizations on key risk identification, prevention and response.
From HumanEvents: A former MF Global employee accused former president William J. Clinton of collecting $50,000 per month through his Teneo advisory firm in the months before the brokerage careened towards its Halloween filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy.
Teneo was hired by MF Global’s former CEO Jon S. Corzine to improve his image and to enhance his connections with Clinton’s political family, said the employee, who asked that his name be withheld because he feared retribution.
From PRNewswire: NEW YORK and LONDON, July 9, 2015 /PRNewswire/ — Teneo Holdings today announced that it has completed the acquisition of Blue Rubicon and StockWell, two of the UK’s leading strategic communications and reputation management firms.
The acquisitions of the two businesses, in addition to Teneo’s existing UK operations, will create one of the largest strategic communications practices in the European market. It will also augment Teneo’s operations in other parts of the world. All members of the Blue Rubicon and StockWell senior management team will continue as part of the Teneo leadership team. Terms of the transactions have not been disclosed.
Blue Rubicon, widely regarded as one of the most progressive strategic communications consultancies to have emerged in London in the last 20 years, provides senior counsel to some of the world’s largest companies as they navigate high-stake issues including succession planning, corporate restructuring, re-launches and post-M&A integration. Founded 15 years ago the firm has been led by Senior Partner, Fraser Hardie, CEO, Gordon Tempest-Hay, Partners Chris Jones and Fiona Joyce. Blue Rubicon today employs more than 225 people operating globally from offices in London, Doha, Dubai and Singapore.
StockWell was founded in 2010 and is led by its three Managing Partners: Tim Burt; Philip Gawith and Richard Holloway. The firm is headquartered in London and has 30 staff. StockWell specializes in providing boardroom level strategic communications advice to leading corporations and individuals across the UK, Europe and beyond.
It is intended that the London operations will be combined and co-located in London in the near future. They will report to Charles Watson in his capacity as Chairman of Teneo International.
“The acquisition of Blue Rubicon and StockWell is a transformational moment for Teneo as we continue to grow across the globe, building on our reputation as one of the world’s leading advisory firms,” said Declan Kelly, Chairman and CEO of Teneo.
****
Then we have Justin Cooper….he was the original person that set up Bill and Hillary’s server(s). Where did he come from? Cooper is a Senior Advisor at Teneo Holdings LLC and a member of the Clinton Foundation.
Even Chelsea Clinton wanted to be hired at Teneo, but a weird collision course was ahead and the intersection got crowded, including the Clinton Global Initiative.
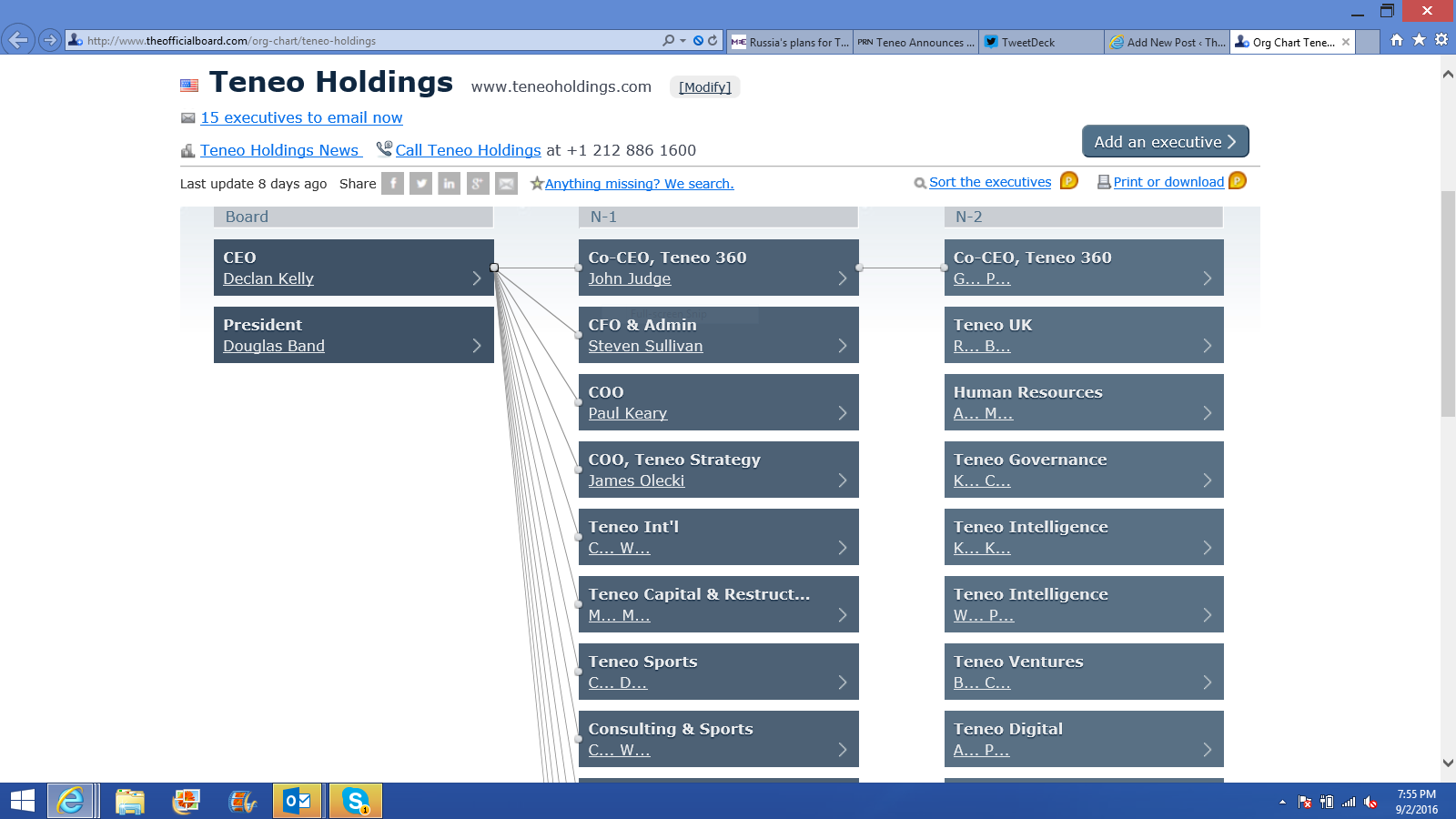
Teneo has divisions that cover the spectrum of all business, industry and government. For a view of division heads click here.
So is there an underlying objective to Teneo’s business model? Yes, it appears to be called ‘activist investments’. As noted here: Dealing with activist investors
On March 19, 2014, members of the Audit Committee Leadership Network (ACLN) met in New York to discuss investor activism, in particular the activism focused on company performance and shareholder value (as opposed to political or social causes).1 In this session, members were joined by Andy Merrill, senior managing director at Teneo Strategy2.
In 2014, Teneo published a lengthy document titled “Where is the World Going”, a comprehensive look at global conditions and submissions for what leaders of industry should and can do. In short, they cannot do what respective and distant government wont allow them to do unless there is ‘activism’ in global governance and of course diplomatic objectives can influence government certainly when it comes to money, power and recognition.
Teneo distinguishes itself in from its competitors in large part through the all-encompassing approach its takes to its services. The latest aspect to the business, Teneo Intelligence, is headed up by a former an ex-CIA and Department of Defense figure and aims to identify trouble spots around the world and analyse their potential effect on global markets.
So, about all those business and industry deals across the globe? Here are but 3 examples:
Hat tip to this site for packaging it all quite nicely and going the long keyboard work. Our friends at Judicial Watch have through legal proceedings provided the documents proving the crowded intersection.
In summary this Fox documentary is a good refresher that remains quite useful especially in light of the FBI releasing the server investigation documents.
Top secret cables revealed that Mrs Clinton, the Secretary of State, even ordered diplomats to obtain DNA data – including iris scans and fingerprints – as well as credit card and frequent flier numbers.
All permanent members of the security council – including Russia, China, France and the UK – were targeted by the secret spying mission, as well as the Secretary General of the UN, Ban Ki-Moon.
Sigh….
