Cant make this up……
Consider again this interview with the three previous Secretaries of Defense under Barack Obama…..
Rice Details U.S. Whole-of-Government Approach to Defeating ISIL
By Jim Garamone DoD News, Defense Media Activity
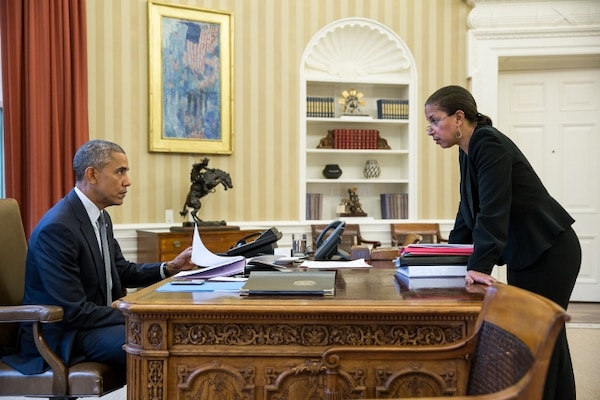

DOWNLOAD HI-RES / PHOTO DETAILS President Barack Obama talks with National Security Advisor Susan E. Rice in the Oval Office prior to a phone call with Russian President Vladimir Putin, Feb. 10, 2015. White House photo by Pete Souza
Susan E. Rice told the cadets and faculty that defeating ISIL is “at the very top of President Obama’s agenda.”
While the terror group is not an existential threat to the United States, she said, it is a danger to Americans and U.S. allies around the globe. Rice pointed to the ISIL attacks in Brussels, Paris, Istanbul, San Bernardino, Jakarta, Nigeria and others. She also highlighted ISIL in Syria and Iraq and the danger it poses to millions of people under its rule.
Dangerous Hybrid
What makes the group dangerous is that “it is essentially a hybrid,” the national security advisor said. ISIL is a terror organization that exploited the chaos of civil war in Syria to attack and occupy large swaths of Syria and Iraq. “At the same time, they have harnessed the power of social media to recruit fighters and inspire lone-wolf attacks,” Rice said.
ISIL is an enormous danger to civilians in the region and is an incredibly destabilizing force in the Middle East, she said, but members of the group are not 10 feet tall.
“This is not World War III or the much-hyped clash of civilizations,” Rice said. “On the contrary, we alienate our Muslim friends and allies — and dishonor the countless Muslim victims of ISIL’s brutality — when people recklessly and wrongly cast ISIL as somehow representative of one of the world’s largest religions.”
ISIL is simply “a twisted network of murderers and maniacs, and they must be rooted out, hunted down and destroyed,” she said, and all aspects of the U.S. government are part of the process to stop them.
Comprehensive Strategy
“For the past year and a half, the president has been leading a comprehensive strategy to destroy ISIL and its ideology of hate,” Rice said. “And, I do mean comprehensive. When we’re sitting around the situation room table, we’re using all aspects of our power — military, diplomacy, intelligence, counterterrorism, economic, development, homeland security, law enforcement. Ours is truly a whole-of-government campaign.”
And it is a global effort, the national security advisor emphasized. “We’ve assembled a broad coalition of 66 partners — from Nigeria and the Arab League to Australia and Singapore,” Rice said.
The anti-ISIL campaign represents an evolution in America’s broader strategy of confronting and defeating terrorism, she said, noting that since 9/11, the United States has learned that not every conflict requires large numbers of ground troops. “Our fight against ISIL is not like Afghanistan or the Iraq War,” she said.
In Syria and Iraq, coalition forces are helping to train indigenous forces, she said. “And, this increasingly dynamic campaign is ideally suited for airpower and the Air Force, utilized smartly in support of our partners on the ground,” Rice added.
The counter-ISIL strategy has four facets, she said. First, it calls for attacking ISIL’s core in Syria and Iraq. Second, the coalition is targeting ISIL’s branches. Third, the coalition is working to disrupt ISIL’s global network. Fourth, the United States is working around the clock to protect the homeland.
Substantial Progress
“It is a complex effort,” the national security advisor said. “It will not be accomplished fully in just a few weeks or months, or even a few years. But day by day, mile by mile, strike by strike, we are making substantial progress. And … we’re going to keep up the momentum.”
Rice detailed the coalition’s plans to continue the pressure on ISIL, beginning with continuing to hammer at the terrorist organization in Iraq and Syria — the so-called core ISIL. Coalition forces have conducted more than 11,500 strikes against core ISIL since starting operations in 2014, she said.
“Due, in large part, to our unprecedented visibility of the battlefield, the coalition air campaign is having a real impact,” Rice said. “Every few days, we’re taking out another key ISIL leader, hampering ISIL’s ability to plan attacks or launch new offensives.”
The strikes also are squeezing ISIL’s finances, which flow from their control of vast oil resources, their extortion and taxation of local populations and their looting and illicit sale of our cultural heritage, she said.
On the Ground
On the ground, the coalition will continue to support local forces in Iraq as they roll back ISIL, the national security advisor said. “So far, they have retaken more than 40 percent of the populated territory that ISIL once held,” she said.
“This fight will continue to require the courage and perseverance of the Iraqi people,” Rice continued. “It will also require the sustained financial support of the international community. It is not enough to win this fight; we must also win the eventual peace.”
Ending the civil war in Syria will go a long way to destroying ISIL, she said. An interagency team of diplomats, military and intelligence officers, working alongside Russia and other international partners facilitated a cessation of hostilities in the country, Rice noted. “This cessation has largely held, but in recent days, we’ve seen a significant uptick in fighting,” she said. “We’re increasingly concerned that the regime’s persistent violations of the cessation — and al-Nusrah’s hostile actions — will undermine efforts to quiet the conflict.”
Assad Must Go
Syrian President Bashar Assad may continue trying to disrupt and delay the good-faith efforts of the international community and the Syrian people to broker a political transition, the national security advisor said. “But he cannot escape the reality that the only solution to this conflict — the only way this ends — is through a political process that brings all Syrians together under a transitional government, a new constitution and credible elections that result in a new government without Assad,” Rice said.

But core ISIL is only part of the problem, she noted. ISIL will flourish in fragile states and lawless regions, Rice said, citing ISIL ally Boko Haram in Nigeria and ISIL’s branches in Libya, on the Arabian Peninsula, in West Africa, in Afghanistan and Pakistan. ISIL has sent envoys “to provide their affiliates with money, fighters — even media training,” Rice said.
In Libya, ISIL threatens not only North African stability, but also sub-Saharan Africa and Europe as well, the national security advisor said.
In Afghanistan and Pakistan, ISIL has established a branch calling itself ISIL in the Khorasan — largely composed of former Afghan and Pakistani Taliban members. “They’ve gained territory in the east and launched attacks in major cities like Jalalabad, though a combination of U.S., Afghan, and Taliban pressure has limited ISIL’s gains,” she said. “As part of the U.S. counterterrorism mission in Afghanistan, President Obama has authorized the Department of Defense to target ISIL in the Khorasan.”
ISIL Affiliates in Yemen
In Yemen, ISIL affiliates have taken advantage of ongoing instability to attack mosques and nursing homes. In Saudi Arabia, ISIL has targeted security forces and civilians. “To address these offshoots, we are deepening our security cooperation with countries in the region,” Rice said. “When President Obama attends the U.S.-Gulf Cooperation Council Summit in Riyadh [Saudi Arabia] next week, ISIL will be at the top of our agenda.”

The United States is working with countries such as Mali, Somalia, Bangladesh, Indonesia and the Philippines, which are countries targeted by the terror group, Rice said. “With smart, sustained investments,” she added, “we have a chance to prevent ISIL from taking root in these disparate corners by assisting our partners in ways as varied as improving local law enforcement, promoting development and countering ISIL’s nefarious narrative.”
ISIL’s narrative is at the heart of dismantling ISIL’s global network, Rice said. The attacks in Paris highlighted the threat of ISIL fighters returning home, she noted. The United States sent “foreign-fighter surge teams” to work with allies as they implement long-term structural reforms to improve intelligence sharing and prevent future attacks, she said.
Homeland Defense
U.S. officials in the homeland are also working to strengthen aviation security and screening, and working with Interpol to share thousands of profiles of suspected fighters, Rice said. “Roughly 45 countries have established mechanisms to identify and flag terrorist travel to Iraq and Syria, and dozens of countries have arrested fighters or aspiring fighters,” she added. “Together with our partners, we’re slowing the flow of foreign terrorist fighters into and out of Iraq and Syria — including sealing almost all the border with Turkey.”
It remains a problem. Since 2011, nearly 40,000 foreign fighters have traveled to Syria from more than 120 countries. “We will continue to do everything in our power to prevent them from returning and launching attacks in our countries,” Rice said.
The United Nations has passed a resolution targeting ISIL’s abuse of the international financial system. The raid last year against Abu Sayyaf, ISIL’s finance chief, yielded a wealth of information on ISIL’s financial vulnerabilities: 7 terabytes of flash drives, CDs, papers and other data, she said. “That’s more than we got out of the bin Laden raid. And, we’re going to continue using that information and other tools to turn off the ISIL funding tap,” Rice said.
Hearts and Minds
The battle against ISIL is a battle for hearts and minds, Rice said. She quoted the president saying, “Ideologies are not defeated with guns; they’re defeated by better ideas.”
The United States is working to expose ISIL’s twisted interpretation of Islam and underscore that ISIL not only is not defending Muslims, but also is killing many innocent Muslims, Rice said. But the United States cannot deliver this message, she said. It has to come from Muslims.
U.S. officials are supporting partners across the globe, including in Saudi Arabia and Malaysia, to get this message across, the national security advisor said. She praised the State Department’s new Global Engagement Center for amplifying anti-ISIL voices internationally, from religious leaders to ISIL defectors.
“Week by week, these voices are eroding ISIL’s appeal,” Rice said. “A new poll shows that nearly 80 percent of young Muslims — from Saudi Arabia to Egypt to Tunisia — are now strongly opposed to ISIL.”
Addressing Conditions
But the president doesn’t want to defeat ISIL only to have another group pop up and take its place, Rice said. “To defeat ISIL’s ideology for good, however, we must acknowledge the conditions that help draw people to ISIL’s destructive message in the first place,” she said. “Around the world, countries and communities — including the United States — must continue working to offer a better, more compelling vision. We must demonstrate, as President Obama has said, that the future belongs to those who build, not those who destroy. Where ISIL offers horror, countries around the world must offer hope.”

Finally, Rice said, it comes down to protecting the homeland. “We’ve hardened our defenses — strengthening borders, airports, ports and other critical infrastructure,” she said. “We’re better prepared against potential bioterrorism and cyberattacks.”
U.S. borders will remain strong, and counterterrorism experts will remain hyper-vigilant, the national security advisor said. “The enduring source of America’s strength, however, comes from upholding our core values — the same enduring values embodied in each one of you at this academy,” Rice said. “It is when people feel persecuted or disempowered that extremism can take hold, so our commitment to the dignity and equality of every human being must remain ironclad.
“In the face of ISIL’s barbarism,” she continued, “America must remain resilient and defiant in our freedom, our openness, and our incredible diversity.”

 Download Image
Download Image  Image details page
Image details page 
