Netanyahu says will not allow Israel to be ‘submerged’ by refugees
Jerusalem (AFP) – Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu on Sunday said he would not allow Israel to be “submerged” by refugees after calls for the Jewish state to take in those fleeing Syria’s war.
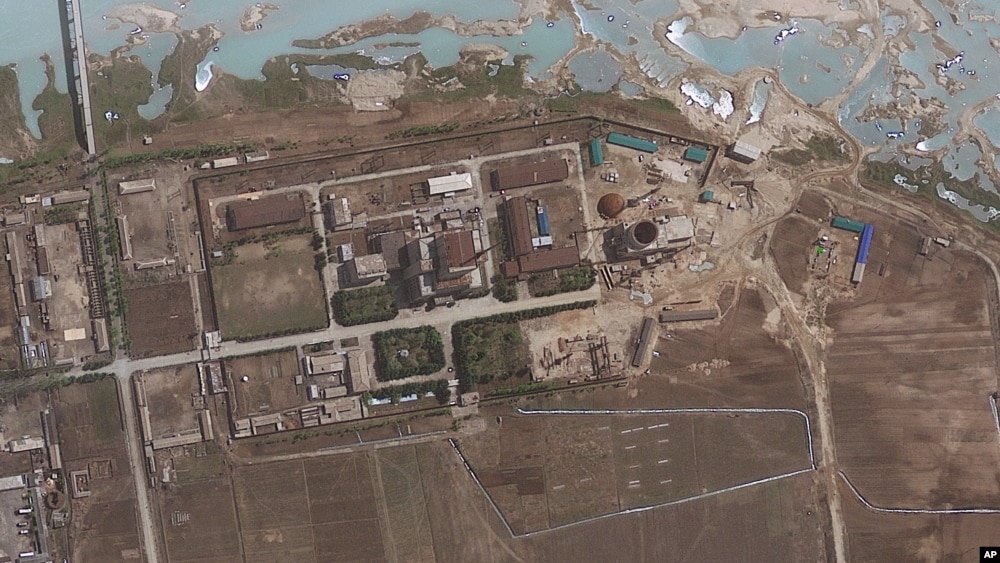
Speaking at the weekly cabinet meeting, Netanyahu also announced the start of construction of a fence along Israel’s border with Jordan, according to his office.
“We will not allow Israel to be submerged by a wave of illegal migrants and terrorist activists,” Netanyahu said.
“Israel is not indifferent to the human tragedy of Syrian and African refugees… but Israel is a small country — very small — without demographic or geographic depth. That is why we must control our borders.”
Opposition leader Isaac Herzog on Saturday said Israel should take in Syrian refugees, recalling the plight of Jews who sought refuge from past conflicts.
Palestinian president Mahmud Abbas also called for Israel to allow Palestinians from refugee camps in Syria to travel to the Palestinian territories, whose external borders are controlled by the Jewish state.
There is already hostility in Israel toward asylum-seekers from Africa and a concerted government effort to repatriate them.
Rights groups say thousands of African asylum seekers have been coerced into “voluntary” departures.
Official figures show 45,000 illegal immigrants are in Israel, almost all from Eritrea and Sudan. Most of those not in detention live in poor areas of southern Tel Aviv, where there have been several protests against them.
– ‘To the Golan heights’ –
The start of construction of the 30-kilometre (19-mile) fence announced by Netanyahu involves extension of a security barrier to part of its eastern border with Jordan in a bid to keep out militants and illegal migrants.
Netanyahu said when it was approved in June that the new fence was a continuation of a 240-kilometre barrier built along the Egyptian border which “blocked the entry of illegal migrants into Israel and the various terrorist movements”.
In its first stage, the new fence is being built along Israel’s eastern border between Eilat and where a new airport will be built in the Timna Valley.
“We will continue the fence up to the Golan Heights,” Netanyahu said.
That would take it into the Israeli-occupied West Bank along the Jordan Valley, an area which is already under Israeli military control but is claimed by the Palestinians as part of their state.
Israel has insisted on maintaining troops in the area in any final peace agreement, a stance completely rejected by the Palestinians who say it would be a violation of their sovereignty and merely perpetuate the occupation.
Israel also has a fence that runs along the Syrian frontier through the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights.
Those fences are in addition to a barrier that runs through the West Bank, which Israel began building during the second Palestinian intifada, or uprising, which lasted from 2000-2005.
Israel seized 1,200 square kilometres (460 square miles) of the Golan from Syria in the 1967 Six Day War and annexed it 14 years later, in a move never recognised by the international community.
***
When it comes to the implications in the Middle East due to unrest, terrorism and war, the threat matrix festers. Israel knows this well as describes by experts below with regard to a post Iran deal at the hands and consequence of Barack Obama and those other P5+1 members.
The Middle East After the Iran Nuclear Deal
Negotiations between Iran and major powers were narrow in scope, focused on limiting Iran’s nuclear program in exchange for relief from nuclear-related sanctions. Nevertheless, the deal they yielded has broader implications for a region strewn with local conflicts that have been exacerbated by the interventions of regional powers. Five experts weigh in on how Middle Eastern states and nonstate actors are calibrating their policies, and what the new regional landscape might portend for conflicts from the Levant to Yemen.

Lebanese supporters of Hezboollah celebrate in May 2014. (Photo: Ali Hashisho/Reuters)
The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) does not announce Iran’s arrival as a regional hegemon, something few among Tehran’s decision-making elite believe Iran has either the ideological or military capacity to achieve. Iranian leaders also know that there is little appetite for such an aggressive posture among a population weary of war with neighbors and hostile relations with world powers. Yet the agreement’s Iranian proponents argue that despite limitations placed on the country’s nuclear program, the deal enhances Iran’s security and consolidates its regional clout.
Major powers learned they must resolve their differences with Iran via diplomatic channels.
Foreign Minister Mohamad Javad Zarif, for example, argues before Iranian audiences that in foreign capitals worldwide in recent years, “Iranophobia” had taken root. He blames the broad-based international sanctions that had been imposed on Iran on a widely held belief that Iran is an aggressive or irrational actor that poses a danger to regional and international security.
But since Iran negotiated on rather than gave up its nuclear program, it demonstrated to major powers that it would not be bullied with military threats and economic sanctions, Zarif and like-minded advocates of the deal argue. The two-year-long nuclear negotiations undermined Iranophobia in many foreign capitals as major powers learned they can—and, indeed, must—resolve their differences with Iran via diplomatic channels rather than by coercion.
There is consensus among the Iranian foreign policy and security establishment that its warnings regarding the destabilization of Syria have proven prescient. They also share the belief that Iran’s domestic politics are the most stable in the region and its foreign policy the most consistent: Iran, they say, pursues systemic stability against antisystemic forces of global terror. The spread of Islamic extremism in the form of the self-proclaimed Islamic State, combined with the election of a government in Iran that ran on a platform of Islamic moderation, has helped advance Iran’s argument that regional issues can only be resolved if it has a seat at the table.
Yet despite a consensus that Iran’s position in the region has been enhanced, the JCPOA is not without its critics in Iran. It allows an inspection regime that violates Iran’s sovereignty and places too much trust in the United States, some argue. Others have slammed the negotiators for concealing the extent of Iran’s concessions and challenged the very notion of compromise with the United States, which, they believe, has not abandoned its ambition of regime change in Tehran, only its coercive tactics. A few even foresee the eventual comeback of coercion, noting that after Libyan dictator Muammar al-Qaddafi gave up his nuclear program, the West intervened militarily.
But the JCPOA’s Iranian proponents scoff at the comparison of the Islamic Republic to one-man dictatorships and insist that the resolution of the nuclear standoff strengthens Iran’s position, gradually opening the way for diplomatic progress on logjams like Syria. Only time—and the adjustments of other significant players in the region—will prove whether this optimistic and benign assessment of Iran’s ascent in the region is correct.
The negotiations deliberately focused solely on Iran’s nuclear program. Now that a deal has been concluded, many are wondering what it might mean for the Middle East, where Iran is involved in many of the region’s conflicts.
A richer Iran is likely to double down on its support for the Assad regime.
Chief among them is Syria. The war there has already killed 250,000 people and displaced nine million. Along with Russia, Iran is Syrian President Bashar al-Assad’s main backer; the United States, Europe, and Gulf states support his opponents. A Syrian peace deal wouldn’t be viable without Iran’s participation. Hence the flurry of diplomatic activity in the past weeks, as countries have tested the waters after the Iran deal.
Iran is pragmatic. Iranian officials have in the past indicated they aren’t wedded to Assad.
Yet while the nuclear deal might, in theory, lead to more open discussions among the many powers with a stake in Syria, in practice Iran shows no sign of ending its support for the regime. Assad himself certainly views it that way: he called the agreement a “victory” for Iran—and, by unspoken extension, for himself.
Even under sanctions and with domestic troubles, Iran has dedicated billions of dollars to the regime’s survival, funding and training pro-regime militias, including the paramilitary National Defense Force and Shia fighters. As sanctions are lifted and Iran has more money, it is likely to spend more to keep the regime afloat.
Although Iran and its adversaries agree that the self-proclaimed Islamic State is a problem, they are divided over what to do about it. Iran sees the group’s expansion as reinforcing its view that the Syrian regime must stay, backing Assad’s claim to be the only party capable of defeating “terrorism” in Syria. Opponents argue that Assad is a cause of Islamic State—by letting extremists out of prison and killing Muslims—and until he goes, it won’t abate.
Any agreement would require assuring Iran that its interests in Syria will remain intact. Iran says it wants stability and the end of Islamic State, but its main interests lie elsewhere: It likes to assert its power, especially vis-a-vis the United States and its allies. And more important to Iran is that it has a route to send weapons to Lebanon, where Hezbollah acts as a strategic deterrent to Israel, a far greater military power than Iran. The United States, Europe, and Gulf powers are not going to agree to that.
Yet Iran’s hegemony in Syria is not assured. Its influence there is more tenuous than it is in Iraq, where Iran backs the government and some militias. Without the large Shia constituency it has in Iraq, Iran’s influence on Syria relies far more on money and pragmatic alliances than natural affinity. A richer Iran is more likely to double down on its support for the regime than promote a reasonable negotiated settlement.
Iran is Hezbollah’s primary benefactor, giving the Lebanese political party and militant group some $200 million a year in addition to weapons, training, intelligence, and logistical assistance. Over the past eighteen months, however, Iran has cut back its financial support to Hezbollah—a collateral benefit of the unprecedented international sanctions regime targeting Iran’s nuclear program, as well as the fall in oil prices.
A newly enriched Hezbollah would be more aggressive at home and abroad.
The cutback has mostly curtailed Hezbollah’s political, social, and military activities inside Lebanon. Its social-service institutions have cut costs, employees have received paychecks late or been laid off, and funding for civilian organizations, such as the group’s satellite television station, al-Manar, has been reduced. By contrast, Hezbollah’s Syria command, which has been a priority for Tehran given its commitment to defending Bashar al-Assad’s regime, has shown no sign of financial hardship.
If nuclear-related sanctions are lifted in whole or in part, an influx of Iranian money will enable Hezbollah to push back against Lebanese political and social movements that are uncomfortable with its intervention in Syria. Lebanon’s political crises, from its inability to select a president to its failure to collect garbage, is a result of this deep sectarian division. An influx of radicalized Sunnis from Syria could bring further instability to Lebanon.
Increased Iranian spending will also benefit Hezbollah’s regional and international operations. The group is no longer limited to jockeying for political power in Lebanon and fighting Israel. With more money, it could step up its aid to Shia militias in Iraq and Yemen in cooperation with Iran, sending small numbers of skilled trainers to bolster local forces and, in some cases, fight alongside them. In Iraq, Hezbollah is training and fighting with Shia militias. Though they are fighting on behalf of the government, their tactics exacerbate sectarian tensions. Its footprint in Yemen is small, but it could expand with additional resources. Hezbollah is already trying to find long-term support for these operations. In Iraq, for example, it is investing in commercial front organizations.
Finally, increased funding could help Hezbollah reconstitute its capabilities beyond the Middle East. The group has expanded its terrorist operations in countries as disparate as Cyprus, Peru, and Thailand.
Hezbollah is busier than ever, especially in Syria, where it is engaged in expensive militant operations and support activities. Meanwhile, the group has expanded its regional activities further afield, straining its coffers even as it has had to cut back its activities in Lebanon. A newly enriched Hezbollah would be more aggressive at home and abroad, challenging less-militant parties across the Lebanese political spectrum and boosting its destabilizing activities outside of Lebanon.
Despite the heterogeneity of interests and perspectives among the six member states of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), they share a broad consensus on the nuclear deal agreed to by major powers and Iran. This common position was expressed in the joint statement issued by GCC foreign ministers and U.S. Secretary of State John Kerry after their August 3 summit in Qatar.
Riyadh has undertaken a major initiative to unite Sunni states in an anti-Iran alliance.
The statement endorses the nuclear agreement, partly because Gulf states hope that the accord could eventually ease regional tensions. Their endorsement is also a recognition that the deal will go forward no matter what they say, and that they see no benefit in joining Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu as the lone international naysayers. Instead, the Gulf states are seeking to maximize the benefits they will accrue by consenting to the arrangement, to which they are not a party even though it will affect their security (whether for good or ill remains to be seen).
The GCC response also insists that Iran cease employing subversive means to extend its influence in the Arab world. The nuclear deal comes as tensions between Iran and major Gulf states, such as Saudi Arabia and the UAE, have reached a historic high.
A newly hawkish Saudi Arabia has demonstrated it is willing to use military force to try to roll back Iran’s influence in the Gulf. The Saudi-led Arab intervention in Yemen has brought GCC forces into direct conflict with the Iran-backed Houthi militia. Riyadh has also undertaken a major initiative to unite Sunni states in an anti-Iran alliance. To this end, Saudi Arabia has reached out to its former antagonists, such as the regional Muslim Brotherhood movement, including Hamas; forged an alliance with Sudan; and strengthened its relations with Turkey.
The Gulf states are hoping that a successful nuclear agreement will strengthen Iranian moderates and eventually make Iran a more responsible regional actor. But they are not counting on that, nor are they relying as much on U.S. leadership as they have in the past.
Gulf countries are moving to strengthen military cooperation with the United States. They are buying new weapons and have received promises of security coordination but are pressing for even stronger commitments. But they are also seeking closer ties to other powers, such as China, France, and Russia, and are developing an independent approach to secure their vital interests.
These interests include preventing Iran from further destabilizing the Arab world by promoting sectarian conflicts and backing armed Shiite groups, including those within Gulf Arab states, as well as ensuring that Iran does not expand its influence in the region at the expense of Arab interests.
If these new tensions come to define the Gulf relationship with Iran and no significant diplomatic steps are taken to create other means of resolving regional crises, the nuclear deal might actually contribute to a more unstable and violent Middle East.
The nuclear agreement is a done deal. Israel must now decide how best to position itself for this new reality in which Iran’s nuclear aspirations have hopefully been postponed, though not eliminated; its regional and international stature has been strengthened by the resolution of the nuclear issue; and its financial ability to carry out its regional ambitions has been increased.
Israel may not be able to continue its policy of noninvolvement in Syria for long.
Many Israeli security experts believe that Israel’s first priority should be to restore strategic cooperation and intimacy with the United States. An important dimension of that would be for Israel to acquiesce to the agreement and use its intelligence capabilities to help ensure that the nuclear inspections regime is implemented.
Assuming the agreement holds, Israel’s biggest strategic concerns will be Iran’s regional ambitions, the rise of the Islamic State and other radical Islamists on its Syrian border and in nearby Iraq, and threats to the stability of Egypt and Jordan. The civil war in Syria has already resulted in attacks on Israel and holds the greatest potential for escalation.
Emboldened by its recent diplomatic success, Iran is likely to pursue its regional objectives with greater intensity and fewer constraints.
Israel may not be able to continue its policy of noninvolvement in Syria for long. The domination of a Syrian rump state by Iran and its Lebanese client, Hezbollah, which has a significant presence along the Golan Heights, would extend the already explosive confrontation with them from Lebanon to Syria and would present an unacceptable danger for Israel; indeed, it has already begun to do so. Hezbollah appears too stretched in Syria to want a confrontation with Israel soon, but this may change.
A takeover of Syria by the self-proclaimed Islamic State or Syrian rebel groups would also prove dangerous. Heinous as it is, Bashar al-Assad’s regime still has many assets to lose in a confrontation with Israel and can thus be deterred. It will take time for non-state actors to develop similar assets.
The borders with Gaza and Egypt remain combustible. After three major conflicts in recent years, Gazans do not appear to want renewed hostilities. Renewed rocket fire is nevertheless likely and will increase Israeli public pressure for Israeli forces “to finish the work” left undone in 2014. Escalation will be especially likely if Iran strengthens its cooperation with Hamas or Palestinian Islamic Jihad. The growing strength of Islamist extremists in the Sinai makes further border incidents with Egypt more likely as well.
Given their fundamental hostility toward Israel, the current confluence of interests with Saudi Arabia and other Gulf Arab states is unlikely to yield significant practical cooperation, media speculation notwithstanding. Turkey will not upgrade relations as long as President Recep Tayyip Erdogan is in power and seeks closer ties with Iran.
The prospects of an agreement with the Palestinians, already bleak, will diminish in a situation of Iranian regional ascendency. Any attempt to restart talks is destined to fail. It would squander U.S. diplomatic capital, which will be needed when more propitious circumstances arise.


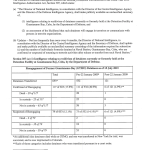


 Lebanese supporters of Hezboollah celebrate in May 2014. (Photo: Ali Hashisho/Reuters)
Lebanese supporters of Hezboollah celebrate in May 2014. (Photo: Ali Hashisho/Reuters)





