Primer: The U.S. holds an enviable lead in pushing artificial-intelligence technology out of labs and into real-world applications. Thank companies like Alphabet (GOOGL), Facebook (FB) and Apple (AAPL) for that.
But China’s government and technology elites aim to overtake the U.S. in AI by 2030 — or so they proclaimed in July at a Beijing political gathering.
Good luck with that.
Yes, China has many strengths as it sets out for worldwide dominance in AI technology. Its internet giants Baidu (BIDU), Alibaba Group Holdings (BABA) and Tencent Holdings (TCEHY) are also pouring money into AI research and hiring top scientists.
China’s huge population will generate massive raw data to train AI systems in how to make predictions. So there’s good reason to think China will make breakthroughs in developing computer algorithms — the software programs that aim to replicate the human ability to learn, reason and make decisions.
China also has a major weakness: a semiconductor industry that still lags the U.S. in making high-end electronic processors. Chinese companies buy AI chips mainly from Nvidia (NVDA), based in Santa Clara, Calif. Intel (INTC), the dominant supplier of brainy chips for personal computers, is pushing fast into AI. More here.
Due to Google employees signing a petition for the Pentagon’s Project Maven, the AI project which is a drone contract. Project Maven is known as Algorithmic Warfare Cross-Functional Team. Google at the time of the contract beat out other bidders including Microsoft, Amazon and IBM. More here on Google.
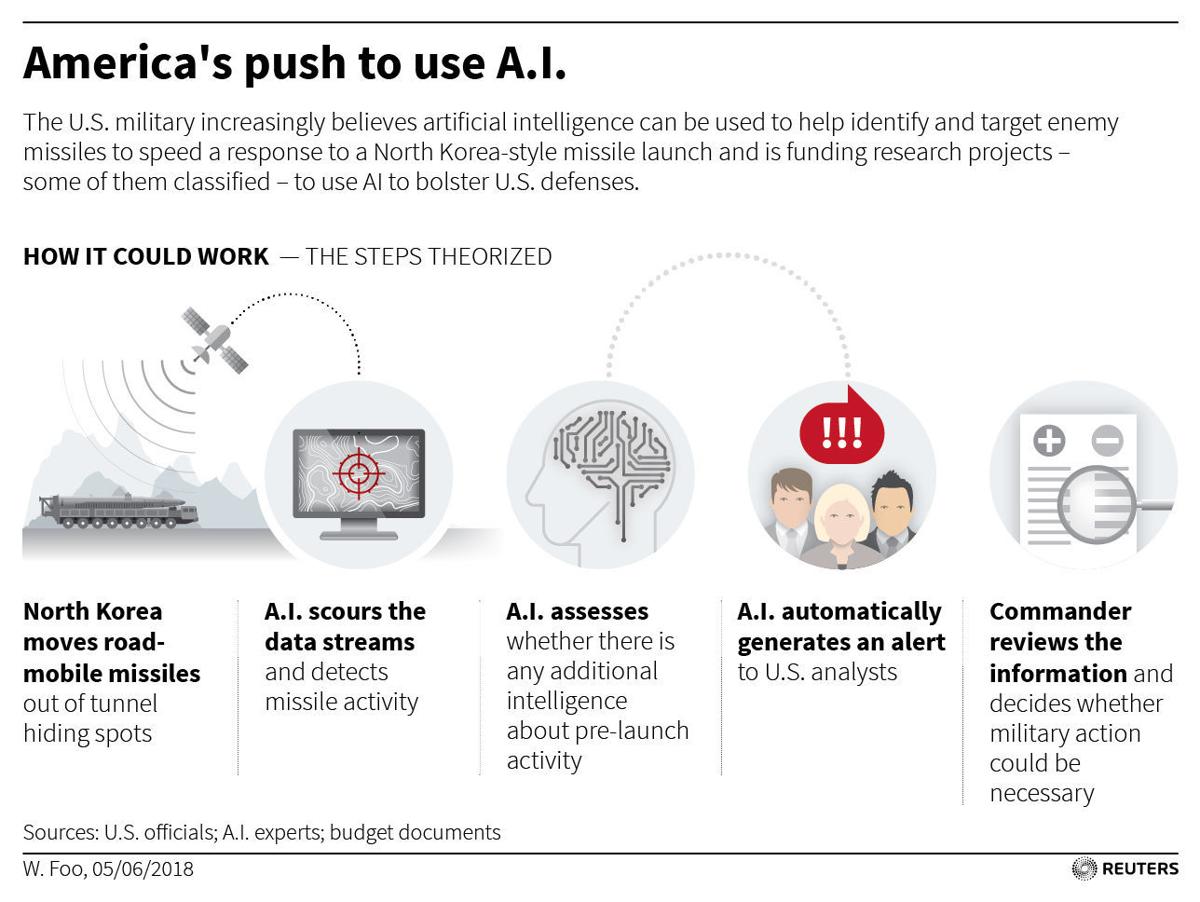
WASHINGTON (Reuters) – The U.S. military is increasing spending on a secret research effort to use artificial intelligence to help anticipate the launch of a nuclear-capable missile, as well as track and target mobile launchers in North Korea and elsewhere.
The effort has gone largely unreported, and the few publicly available details about it are buried under a layer of near impenetrable jargon in the latest Pentagon budget. But U.S. officials familiar with the research told Reuters there are multiple classified programs now under way to explore how to develop AI-driven systems to better protect the United States against a potential nuclear missile strike.
If the research is successful, such computer systems would be able to think for themselves, scouring huge amounts of data, including satellite imagery, with a speed and accuracy beyond the capability of humans, to look for signs of preparations for a missile launch, according to more than half a dozen sources. The sources included U.S. officials, who spoke on condition of anonymity because the research is classified.
Forewarned, the U.S. government would be able to pursue diplomatic options or, in the case of an imminent attack, the military would have more time to try to destroy the missiles before they were launched, or try to intercept them.
“We should be doing everything in our power to find that missile before they launch it and make it increasingly harder to get it off (the ground),” one of the officials said.
The Trump administration has proposed more than tripling funding in next year’s budget to $83 million for just one of the AI-driven missile programs, according to several U.S. officials and budget documents. The boost in funding has not been previously reported.
While the amount is still relatively small, it is one indicator of the growing importance of the research on AI-powered anti-missile systems at a time when the United States faces a more militarily assertive Russia and a significant nuclear weapons threat from long-time foe North Korea.
**“What AI and machine learning allows you to do is find the needle in the haystack,” said Bob Work, a champion of AI technology who was deputy defense secretary until last July, without referring to any individual projects.
One person familiar with the programs said it includes a pilot project focused on North Korea. Washington is increasingly concerned about Pyongyang’s development of mobile missiles that can be hidden in tunnels, forests and caves. The existence of a North Korea-focused project has not been previously reported.
While that project has been kept secret, the military has been clear about its interest in AI. The Pentagon, for example, has disclosed it is using AI to identify objects from video gathered in its drone program, as part of a publicly touted effort launched last year called “Project Maven.”
Still, some U.S. officials say AI spending overall on military programs remains woefully inadequate.
AI ARMS RACE
The Pentagon is in a race against China and Russia to infuse more AI into its war machine, to create more sophisticated autonomous systems that are able to learn by themselves to carry out specific tasks. The Pentagon research on using AI to identify potential missile threats and track mobile launchers is in its infancy and is just one part of that overall effort.
There are scant details on the AI missile research, but one U.S. official told Reuters that an early prototype of a system to track mobile missile launchers was already being tested within the U.S. military.
This project involves military and private researchers in the Washington D.C. area. It is pivoting off technological advances developed by commercial firms financed by In-Q-Tel, the intelligence community’s venture capital fund, officials said.
In order to carry out the research, the project is tapping into the intelligence community’s commercial cloud service, searching for patterns and anomalies in data, including from sophisticated radar that can see through storms and penetrate foliage.
Budget documents reviewed by Reuters noted plans to expand the focus of the mobile missile launcher program to “the remainder of the (Pentagon) 4+1 problem sets.” The Pentagon typically uses the 4+1 terminology to refer to China, Russia, Iran, North Korea and terrorist groups.
TURNING TURTLES INTO RIFLES
Both supporters and critics of using AI to hunt missiles agree that it carries major risks. It could accelerate decision-making in a nuclear crisis. It could increase the chances of computer-generated errors. It might also provoke an AI arms race with Russia and China that could upset the global nuclear balance.
U.S. Air Force General John Hyten, the top commander of U.S. nuclear forces, said once AI-driven systems become fully operational, the Pentagon will need to think about creating safeguards to ensure humans – not machines – control the pace of nuclear decision-making, the “escalation ladder” in Pentagon speak.
“(Artificial intelligence) could force you onto that ladder if you don’t put the safeguards in,” Hyten, head of the U.S. Strategic Command, said in an interview. “Once you’re on it, then everything starts moving.”
Experts at the Rand Corporation, a public policy research body, and elsewhere say there is a high probability that countries like China and Russia could try to trick an AI missile-hunting system, learning to hide their missiles from identification.
There is some evidence to suggest they could be successful.
An experiment by M.I.T. students showed how easy it was to dupe an advanced Google image classifier, in which a computer identifies objects. In that case, students fooled the system into concluding a plastic turtle was actually a rifle. here
Dr. Steven Walker, director of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), a pioneer in AI that initially funded what became the Internet, said the Pentagon still needs humans to review AI systems’ conclusions.
“Because these systems can be fooled,” Walker said in an interview.
DARPA is working on a project to make AI-driven systems capable of better explaining themselves to human analysts, something the agency believes will be critical for high stakes national security programs.
‘WE CAN’T BE WRONG’
Among those working to improve the effectiveness of AI is William “Buzz” Roberts, director for automation, AI and augmentation at the National Geospatial Agency. Roberts works on the front lines of the U.S. government’s efforts to develop AI to help analyze satellite imagery, a crucial source of data for missile hunters.
Last year, NGA said it used AI to scan and analyze 12 million images. So far, Roberts said, NGA researchers have made progress in getting AI to help identify the presence or absence of a target of interest, although he declined to discuss individual programs.
In trying to assess potential national security threats, the NGA researchers work under a different kind of pressure from their counterparts in the private sector.
“We can’t be wrong … A lot of the commercial advancements in AI, machine learning, computer vision – If they’re half right, they’re good,” said Roberts.
Although some officials believe elements of the AI missile program could become viable in the early 2020s, others in the U.S. government and the U.S. Congress fear research efforts are too limited.
“The Russians and the Chinese are definitely pursuing these sorts of things,” Representative Mac Thornberry, the House Armed Services Committee’s chairman, told Reuters. “Probably with greater effort in some ways than we have.”