There’s a reason a 76-year-old woman with a broken femur had to wait 95 minutes for an ambulance at the main TSA checkpoint in the middle of the nation’s busiest airport over the summer.
Half of Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport’s fleet of fully-staffed EMS ambulances were 500 miles away.
11Alive’s investigative team tracked the airport’s Medic 1 and Medic 2 ambulances to the back lot of a factory in Ohio, where Atlanta Fire & Rescue had sent them for extended rebuilds with no replacements ready.
We were told at the time when those two ambulances went into the shop that they will only take 90 days to get it back in service,” Airport General Manager Balram Bheodari told the Atlanta City Council Transportation Committee on Aug. 11. “However, because of the disruption of the supply chain, we were informed it would take 180 days to get those ambulances back,” Bheodari testified.
But the city was told the ambulances would be out of service for 240 days, according to internal documents obtained by The Reveal through public records requests.
The vendor’s written quote with the 240-day estimate was delivered to the city in November of last year, six months before the ambulances were sent to Ohio. Both Medic 1 and Medic 2 were sent for refurbishment at the same time, further reducing available ambulances at Hartsfield-Jackson, the nation’s busiest airport.
The airport had purchased new ambulances in the past, which can replace the old units with no loss of service. However, it’s not clear why the city chose a lengthy rebuild instead, or why both units were sent to Ohio simultaneously instead of one at a time.
Crazy…but then again…emergency rooms cant handle patients anyway as noted below.
LONG BEACH, Long Island (WABC) — The emergency department at a Nassau County hospital has temporarily closed due to nursing staff shortages as a result of New York’s vaccine mandate.
Officials at Mount Sinai South Nassau said Monday that all other options were exhausted before the decision was made to close the ER, starting at 3 p.m.
Instead, patients in need of emergency care will be directed to the hospital’s main campus in Oceanside. An ambulance will be stationed at the ER at all times for the duration of the closure.
The closure will last for up to four weeks and could be expanded, depending on staff availability.
***
Hospitals and nursing homes around the U.S. are bracing for worsening staff shortages as state deadlines arrive for health care workers to get vaccinated against COVID-19.
With ultimatums taking effect this week in states including New York, California, Rhode Island and Connecticut, the fear is that some employees will quit or let themselves be fired or suspended rather than get the vaccine.
“How this is going to play out, we don’t know. We are concerned about how it will exacerbate an already quite serious staffing problem,” said California Hospital Association spokesperson Jan Emerson-Shea, adding that the organization “absolutely” supports the state’s vaccination requirement. source
***
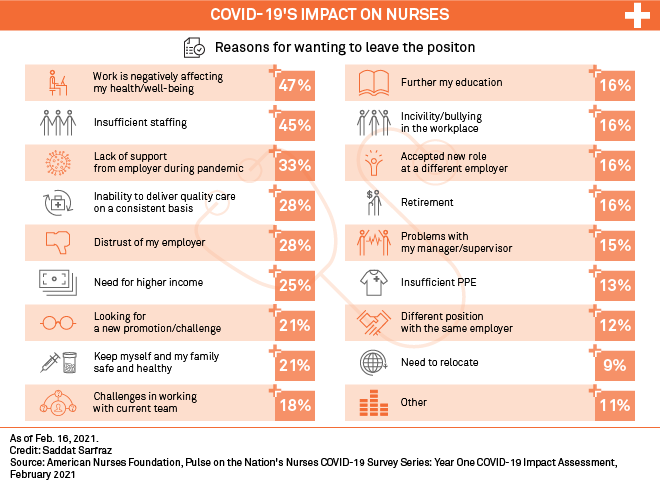
Cyndy O’Brien, an emergency room nurse at Ocean Springs Hospital on the Gulf Coast of Mississippi, could not believe her eyes as she arrived for work. There were people sprawled out in their cars gasping for air as three ambulances with gravely ill patients idled in the parking lot. Just inside the front doors, a crush of anxious people jostled to get the attention of an overwhelmed triage nurse.
“It’s like a war zone,” said Ms. O’Brien, who is the patient care coordinator at Singing River, a small health system near the Alabama border that includes Ocean Springs. “We are just barraged with patients and have nowhere to put them.”
The bottleneck, however, has little to do with a lack of space. Nearly 30 percent of Singing River’s 500 beds are empty. With 169 unfilled nursing positions, administrators must keep the beds empty.
Nursing shortages have long vexed hospitals. But in the year and a half since its ferocious debut in the United States, the coronavirus pandemic has stretched the nation’s nurses as never before, testing their skills and stamina as desperately ill patients with a poorly understood malady flooded emergency rooms. They remained steadfast amid a calamitous shortage of personal protective equipment; spurred by a sense of duty, they flocked from across the country to the newest hot zones, sometimes working as volunteers. More than 1,200 of them have died from the virus. source
CVS changing the business model could be a clue of what is to come –>
CVS announced its plans to begin closing its doors–about 900 locations across the country. Though that looks like a lot, it’s only 10 percent of the company’s retail locations. Though don’t expect the remaining 90 percent to look 100 percent like CVS stores as we know them. Because the big news is really less about its closures and more about what’s to come for the future of the pharmaceutical retailer. And that’s the accessibility of healthcare services across the nation. What CVS is doing is exactly what it set out to do when it first launched nearly six decades ago in 1963.
In the words of the company’s mission, its goal is to “make high-quality health and pharmacy services safe, affordable and easy to access.”
This is a crucial reminder to businesses everywhere: growth doesn’t mean getting bigger, it means getting better. That does not mean getting better at everything, as many are compelled to do. But getting better at what matters most: your core offering. Because it’s also the core reason customers choose your business over the alternatives. And in the case of the pharmaceutical retailer, that’s healthcare.
Your local CVS will no longer necessarily be a place to go when you realized you’re out of milk or to pick up a greeting card–and never mind a late-night destination to grab that 6-pack when no other stores nearby are still open. But your local CVS will be turned into “destinations that offer a range of health-care services, from flu shots to diagnostic tests,” according to the company’s news release.
In other words, a place to go for all things health–as one would expect a pharmacy to be. However, it had become a company that wore many hats. Not only does it serve as a drug store, but also as a convenience store, a grocery store, and in some places, even as a liquor store. With so many revenue channels, there were a number of ways in which the company could grow.
For example, in an effort to expand it could have worked to more directly compete with Walmart, which also offers in-store pharmacies. Or it could have gone after the eCommerce giant, Amazon, which acquired PillPack and entered the pharmaceutical space with its own online pharmacy.
But in a wise–and evidently strategic–decision, it opted to expand in terms of depth. In other words, rather than continuing to be a jack of all trades, it will focus on being the master of easily accessible healthcare And to make strides towards this decision that reinforces its mission, it’s stepping away from offering the breadth of its current offerings. After all, cigarettes and scratch tickets aren’t exactly synonymous with health. source

 Policies and procedures are NOT law by the way…
Policies and procedures are NOT law by the way…


 She authored this item in
She authored this item in 
